The Cool Tech Behind Earthbag Homes (How Long Will It Last?)

Image courtesy of CalEarth.
Did you know you can build a home with only a few lengths of barbed wire, earthbags, a shovel, and the earth beneath your feet?
This is the earthbag building technique – one of the sustainable construction methods intended to minimize the construction industry’s impact on the environment. But what exactly is the technology behind earthbag homes, and how long can we expect them to last?
As an eco-conscious homeowner or developer, you want to know if earthbag building helps reverse the impacts of conventional construction on the environment.
Simply put, you want to ascertain that the technology behind earthbag building is eco-friendly and resource-efficient throughout the building’s lifecycle.
In the rest of this article, I’ll discuss the cool tech behind earthbag homes and why people are leveraging this technique. I’ll also discuss how long you should expect an earthbag home to last.
Let’s get started!
The Evolution of Earthbag Building

Earthbag construction is a building technology attributed to Nader Khalili, the founder of the California Institute of Earth Art and Architecture (Cal-Earth). The technique is based on the principles of military sandbag construction, albeit with a few modifications.
Khalili’s motivation behind this construction technology was to help solve the housing shortage problem. The idea was to educate people on environmentally sustainable building designs that are affordable and long-lasting.
Nader established the Cal-Earth institute to achieve his goal of educating people about sustainable housing solutions. In the institute, he developed building technologies such as earthbag and superadobe construction to help people build energy-efficient and strong structures quickly.
The Technology Behind Earthbag Homes
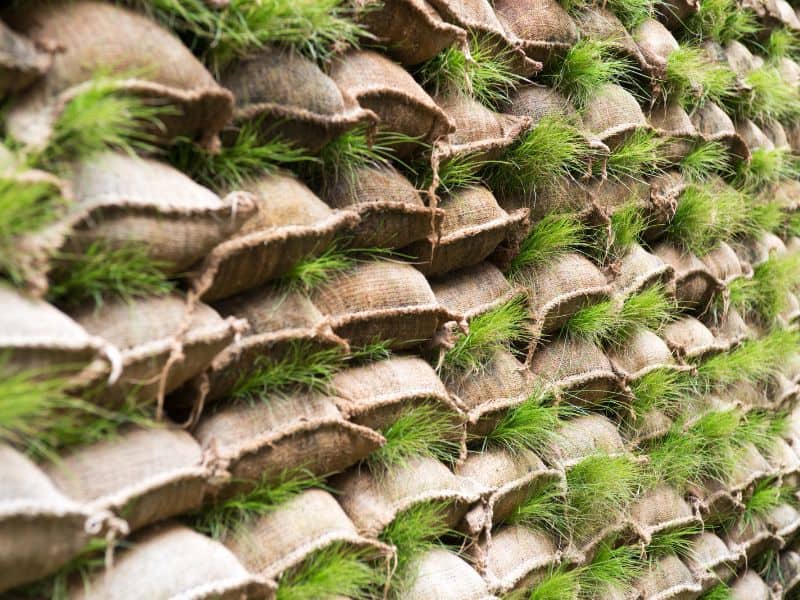
The basic technology behind earthbag homes is filling sandbags with earth and arranging them in layers to create walls. The motivation behind this technique was the military bunkers built using the same method of filling sandbags with soil and stacking them.
Earthbag building is both monolithic and self-supporting. This means it’s constructed in one complete mass, and the walls hold their weight without external support.
The following are the main materials used in earthbag construction:
- Earthbags: Woven or continuous polypropylene bags, burlap sacks, or mesh tubes to contain the earth.
- Soil: It’s usually excavated onsite and must contain a mix of sand, gravel, clay, and silt.
- Amendments for soil mixture: Hydraulic or hydrated lime, gravel, Portland cement, or fly ash.
- Tamps: Hand tampers that create a more uniform wall structure.
- Barbed wire: Placed between layers of earthbags to add strength and stability to the walls.
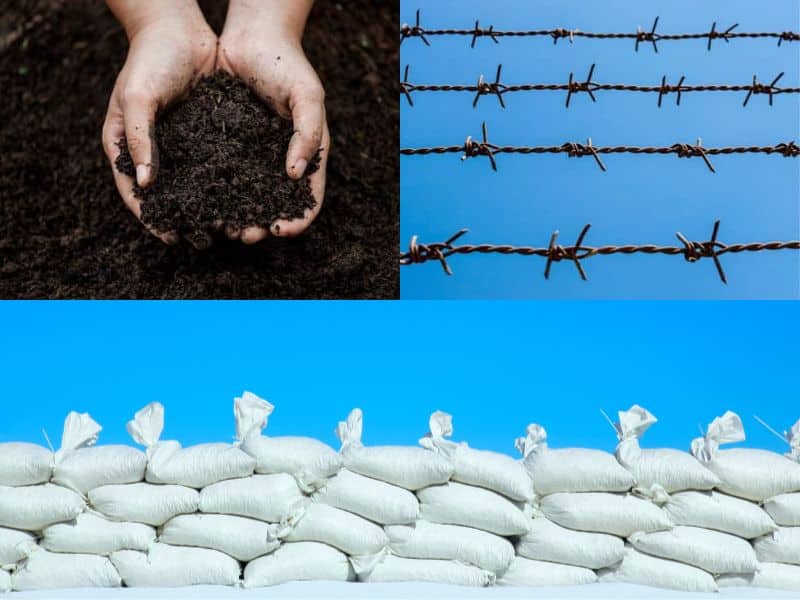

Earthbag Building Procedure
The earthbag building technology entails the following procedure:
Laying the Foundation
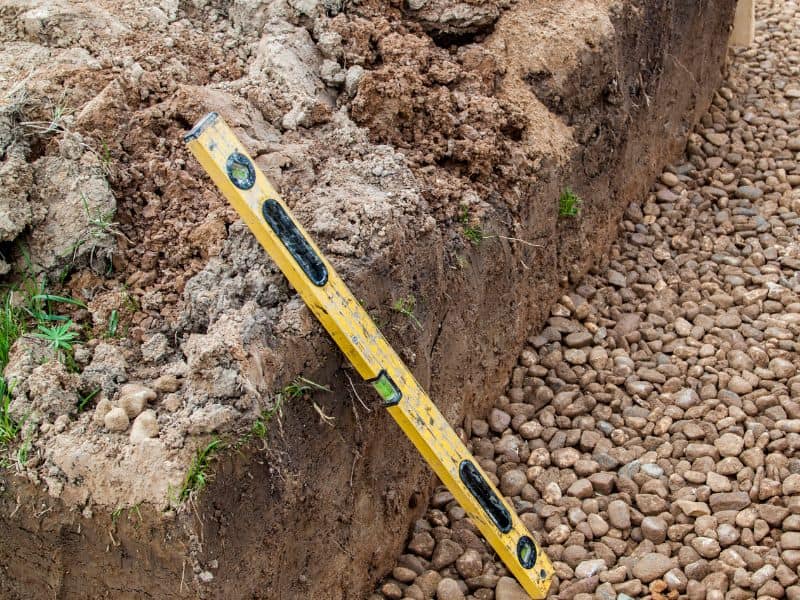

A rubble trench foundation is preferred to keep the floors and walls of the building dry. It also minimizes shock transfer to the walls, making the structure more earthquake-resistant.
The foundation contains several earthbag courses ranging between 4 and 8 inches (10.16 and 20.32 cm). The height of these courses is determined by the size of the bags, the amount of fill, and the compaction degree. Most earthbags have widths ranging between 9 and 24 inches (22.86 and 60.96 cm).
Two strands of barbed wire are laid between each course within the foundation. These wires serve to prevent the bags from sliding on top of each other.
It’s worth mentioning that foundations vary based on the site’s conditions. For instance, rocks are preferred as fill material in a rainy locale to promote drainage.
Preparing the Soil Mixture
The soil mixture should contain a good ratio of sand, clay, silt, gravel, and sometimes stabilizing amendments like lime or cement.
A rule of thumb is to add stabilizers like sodium carbonate, cement, or lime to a mixture containing 70% sand and 30% clay.
It’s not advisable to use topsoil because it contains rotting leaves and other substances–it can rot and compress when used in earthbags.
Subsoil is preferred since it doesn’t have organic matter and humus content. It consists of sand, silt, and clay–the best components for earthbag building.
Filling the Bags
Now that the soil mixture is ready, it’s time to fill the bags. This labor-intensive process entails filling each bag manually and stitching it closed.
After stitching the bags, they are tamped with a hand tamper to ensure sufficient compaction.
Staggering the Filled Earthbags
The next step is to stagger the earthbags like masonry blocks as they are stacked to ensure structural integrity and strength.
Staggering requires overlapping the earthbags by half their width as each course is laid. The process helps distribute the load evenly, prevents sliding, and increases wall stability.
Moreover, the earthbags are aligned according to a string line to keep the level of the walls and ensure they are true to the plan.
Adding Barbed Wire
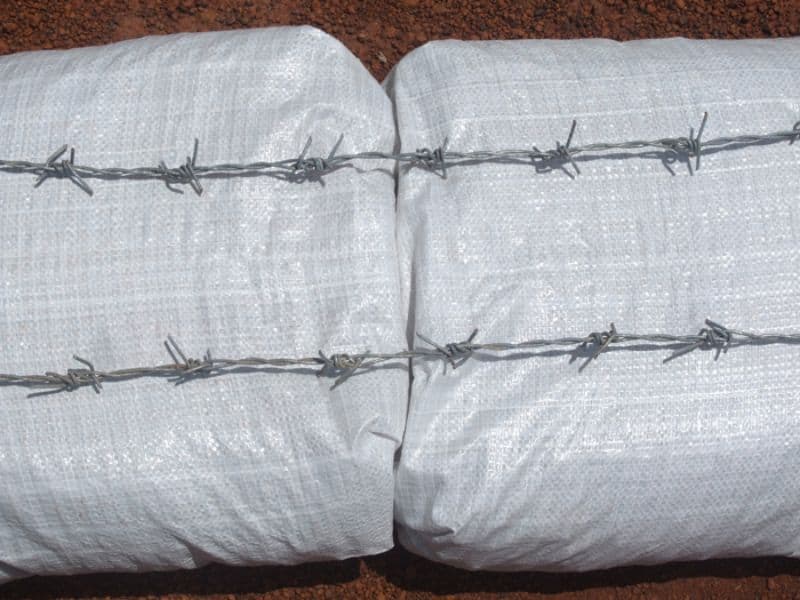

Barbed wire is used to add strength and stability to the walls. Two strands are placed between each course of earthbags and tamped down.
The wire helps bind the bags together to prevent them from sliding laterally. It also ensures that the foundation is strong enough to resist seismic activity.
Each course is tamped down to form a uniform wall structure. New layers are added to the top while creating formwork for doors and windows.
Roofing
Roofing an earthbag home can be done in the following ways:
- Wooden trusses and rafters.
- Wood/steel columns, beams, and purlins.
- Metal trusses and rafters.
A skillion roof with horizontal joists running along the length of the building is preferred for beginners. The joists form a support that pulls the structure together to prevent the earthbags from falling outwards. Some builders top the joists with corrugated iron or strand board with a membrane.
Whichever option is chosen, it’s designed to support the weight of the roofing material. It’s also important to factor in the weight of snow or any rainwater that might collect on the roof.
Plastering
Finally, the bags’ top layer is plastered using adobe or cement stucco.
The stucco is a final protective coating that keeps out water, prevents cracks, and adds insulation to the home. It also gives the structure an aesthetically pleasing look.
Why People Build With Earthbags
Earthbag building is gaining popularity, and many people will adopt this approach for the following reasons:
Affordability
According to research, more than 70 percent of Americans can’t afford contractor-built, code-enforced homes. Therefore more people are shifting to natural materials like earthbags to build houses.
Unlike conventional methods, earthbag building is affordable and costs between $7 and $15 per square foot.
Sustainability

Conventional construction methods that rely on concrete and steel are responsible for up to 50% of climate change. Moreover, these methods contribute immensely towards the depletion of non-renewable natural resources such as fossil fuels and natural forests.
As if that were not enough, traditional construction methods contribute to air, water, and land pollution.
On the contrary, earthbag building is a sustainable technique that conserves the environment.
Earthbag construction has the following sustainable characteristics:
- Reduces waste generation.
- Lessens demand for non-renewable energy sources.
- Increases use of locally-supplied materials.
- Increases the use of environmentally-friendly materials.
- Less energy consumption due to excellent insulation and thermal properties.
Ability to Withstand Disasters
More people will build with earthbags due to their ability to withstand disasters such as floods, fires, vermin, wind, and earthquakes.
For instance, when a 7.8-magnitude earthquake struck Nepal in 2015, more than 600,000 structures were destroyed. However, 55 earthbag buildings survived without structural damage.
How Long Do Earthbag Homes Last?

Earthbag homes will last more than 100 years, provided they are protected from rain and water. Waterproofing the walls with plasters like stucco is essential for prolonging the lifespan of an earthbag home.
Moreover, regular maintenance and proper care will help retain an earthbag home’s integrity for longer. To keep your structure in great shape, apply stucco or lime plaster with a fresh application of lime wash every 1-2 years to renew its protective coating.
It’s also advisable to install a roof with extended eaves to keep water away from the walls.
Final Thoughts
The cool tech behind earthbag homes is a testament to human ingenuity and creativity in finding sustainable housing solutions.
Using earth as a sustainable building material, combined with the latest construction techniques, results in sturdy and durable homes that can last for generations.
If you’re looking to build an earthbag home, here are the best places to buy your earthbag building supplies.